Authentication through Active Directory integration
ThoughtSpot enables you to set up integration with LDAP using Active Directory. After successful setup, you can authenticate users against a secure LDAP server.
You can use ThoughtSpot’s integration with Active Directory for user authentication. By default, local authentication is enabled. You can also configure integration with LDAP through Active Directory, allowing you to authenticate users against an LDAP server. ThoughtSpot doesn’t support any other LDAP authentication.
You can configure the Active Directory integration through the Admin Console.
Configuration prerequisites
Before you configure ThoughtSpot for Active Directory, collect the following information:
❏ |
|
❏ |
|
❏ |
|
❏ |
|
❏ |
URL
Required to connect to Active Directory.
For example, ldap://ad.yourdomain.local:389 or ldap://ad.yourdomain.local:636
Domain name
Default domain under which users who want to be authenticated against Active Directory reside. When a user logs in with a username, the default domain is added to the username before sending it to the LDAP server. If users reside in multiple sub-domains, you can still designate one of them as the default. Authentication against multiple domains is not supported.
Users who don’t belong to the default domain must explicitly qualify their username when they sign in.
For example: username@ad.yourdomain.local
Search base
LDAP search base. The scope of searching user information, like email and Display name, within AD.
Automatically add LDAP or AD users in ThoughtSpot? (yes/no)
If you choose 'yes', new users are automatically created within ThoughtSpot when successfully authenticated against AD. ThoughtSpot doesn’t cache passwords for AD-authenticated users.
If you choose 'no', users have to be manually created with a dummy password as a placeholder in ThoughtSpot before they can sign in.
The username you specify when creating the LDAP-authenticated user manually in ThoughtSpot has to be domain qualified, for example: username1@ad.yourdomain.local.
In order to sign in to ThoughtSpot, the user has to exist in ThoughtSpot independent of whether that user is authenticated against AD or against ThoughtSpot’s internal authentication.
SSL
If you want to use SSL, you must obtain the SSL certificate from an issuing authority. When you select yes, ThoughtSpot prompts you to enter the certificate and certificate alias.
If AD servers are behind a load balancer, you must procure the SSL certificate to identify ThoughtSpot to the load balancer. The communication after the load balancer is non-secure. ThoughtSpot doesn’t support a scenario where multiple AD servers provide their own SSL certificates.
Configure Active Directory
ThoughtSpot Training
For best results, we recommend that you take the following ThoughtSpot U course: Active Directory.
See other training resources at ThoughtSpot U.
Navigate to the Admin Console by clicking on the Admin tab from the top navigation bar. Select LDAP/AD from the side navigation bar that appears.
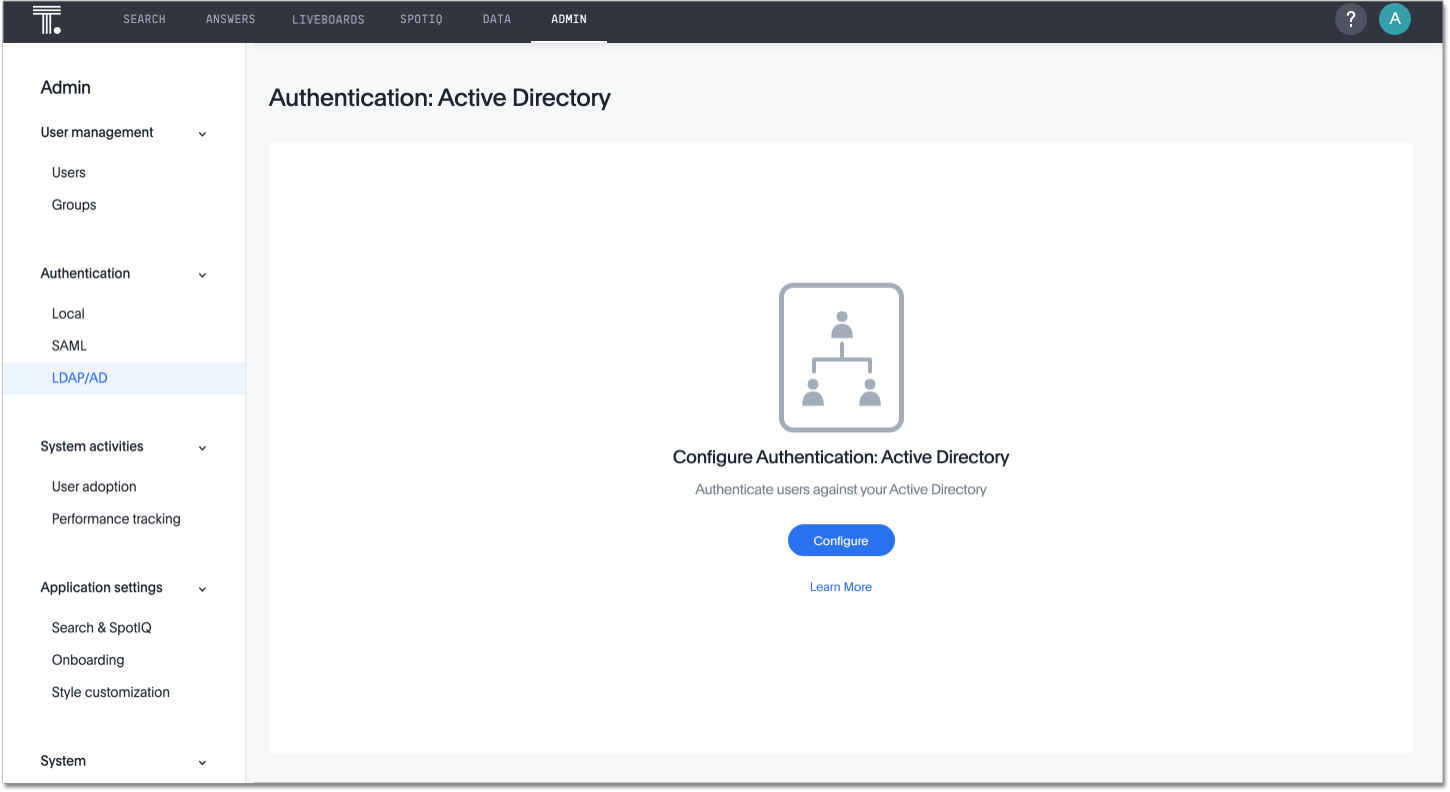
Click the Configure button in the middle of the screen, and add your information based on the information you collected in the prerequisites.
| If you configure authentication through Active Directory, you cannot also configure authentication through SAML. |
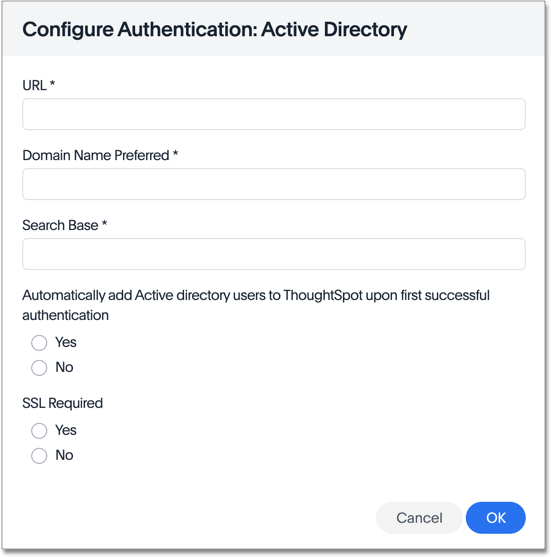
If you select yes for SSL required, ThoughtSpot prompts you to enter the SSL certificate and certificate alias. The certificate alias is a unique name you make up for your SSL certificate, in string format. If you replace the SSL certificate, you need a new certificate alias.
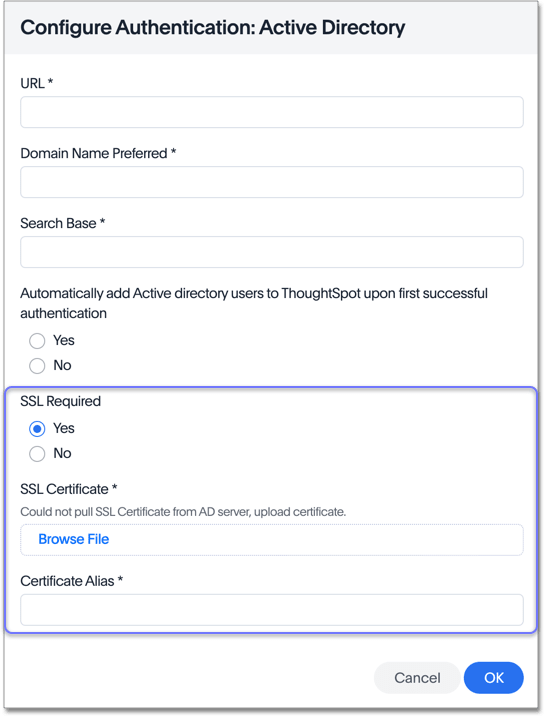
After you add all your information, click OK.
| ThoughtSpot adds external users, or users that authenticate through SAML or Active Directory, to the all group by default. This group has no privileges. You must manually assign users to ThoughtSpot groups to give them privileges, such as can upload user data, or can manage data. |



