Create a relationship
A join combines columns from one or more sources in your data by using matching values. By defining relationships between your sources, you create a new, richer set of data that you can use to answer your business questions. Choose a column to join on that both tables contain (for example, employee ID or product key). This process creates a generic join between the table or view and the other table, view, or worksheet on the column you specify.
| If you want to create a primary key/foreign key relationship, you need to use TQL rather than the web interface. |
Join types
ThoughtSpot supports the following join types: Inner, Left Outer, Right Outer, and Full Outer. You can choose a join type when creating or editing a join through the ThoughtSpot web interface.
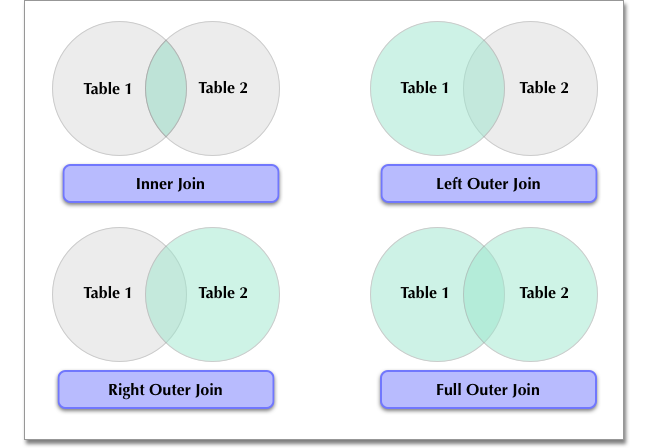
ThoughtSpot defaults to the inner join type, which returns results for data with matching values in both the origin table (Table 1) and the target table (Table 2).
Left outer joins return results for all values from Table 1, and any matching values from Table 2.
Right outer joins return results for all values from Table 2, and any matching values from Table 1.
Full outer joins return results for all values from either Table 1 or Table 2.
Join cardinality
When creating the join, you must also identify its cardinality: Many:1, 1:Many, or 1:1.
A Many:1 cardinality defines a join where multiple values in the origin table (Table 1) correspond to one value within the target table (Table 2). A join between a product table and a product category table shows multiple products that match each category.
A 1:Many cardinality defines a join where one value in the origin table corresponds to multiple values within the target table.
A 1:1 cardinality defines a join where one value in the origin table corresponds to a single value within the target table (for example, employee name and employee ID).
You must create a join between columns in two data sources that contain the same data type, with the same meaning. That is, they must represent the same data. Normally, you can make this kind of link from a fact table column to a column in a dimension table that uniquely identifies a logical entity in your data such as Employee ID for a person, Product ID for a product, or Date Key for a specific date in a date lookup table.
Possible joins
You must have either the Can administer ThoughtSpot or the Can manage data privilege to create a join relationship. If you’re not an administrator, you also need edit permissions on the table, view, or worksheet.
You can join any data object to another object, with the following 2 restrictions:
-
You can only join a worksheet to a user-uploaded CSV table.
-
You cannot join objects across connections. This means that you cannot join an object that is part of one connection to an object in a different connection.
| If you create joins at the table level, and then create a worksheet that uses the columns from the table, the settings are inherited from the table at the point in time that the worksheet is created. If you then go back and change the settings at the table level, your changes won’t be reflected in the worksheet. If you want the worksheet to have the changes you made at the table level, you must drop those columns from the worksheet and re-add them. |
Creating join relationships
Creating a join from a table
To create a table join through the web interface:
-
Select Data in the top menu, and choose Tables.
-
Find your table through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
To select the table for adding joins, click its name in the list. You will see the Columns view of the table.
-
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins from the table appears.
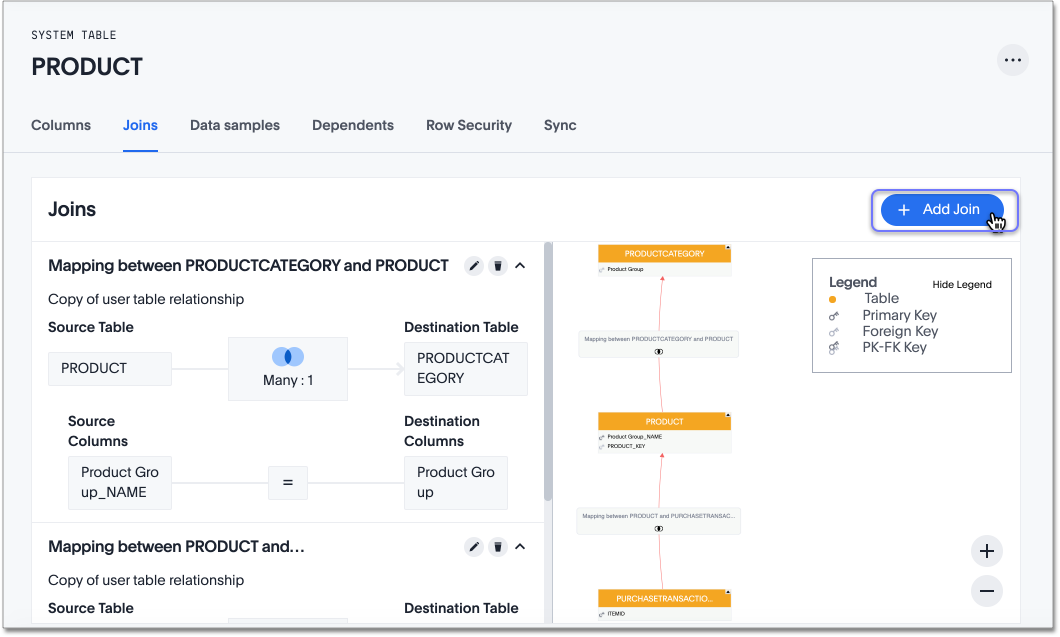
-
Select the + Add Join button on the upper-right side of the screen. The Create Join page appears.
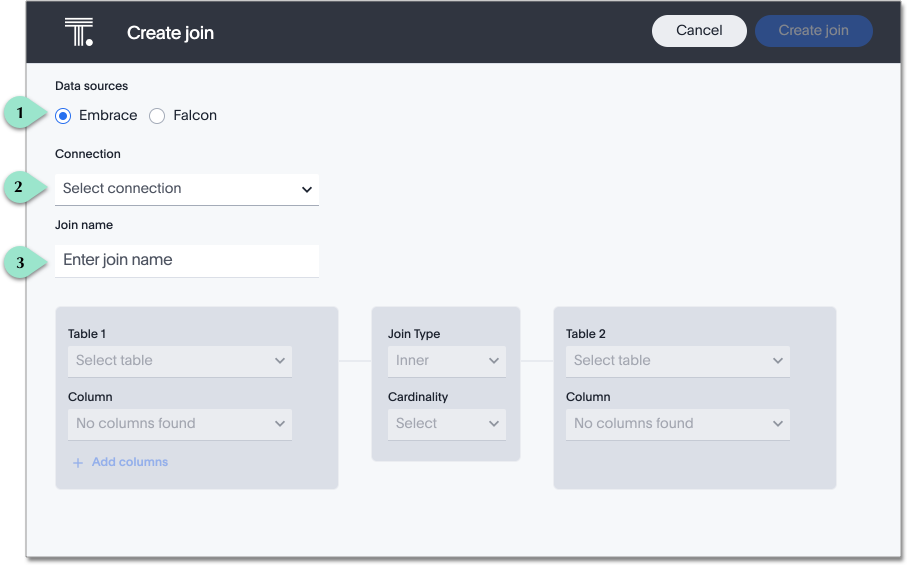
Legend Action 1.
Select the data source of your table, either Embrace, or Falcon.
2.
Choose your connection from the dropdown Connection menu. You can only create joins between data sources uploaded through the same connection.
3.
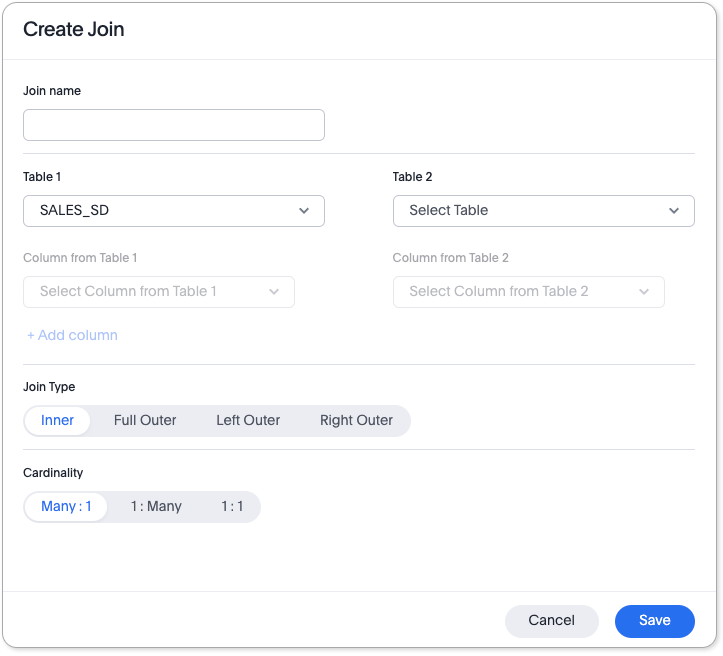
[Optional] Select Enter join name to name your join. Note that ThoughtSpot automatically names joins using the following syntax: [OriginDataSourceName] to[DestinationDataSourceName]. You can always enter a more meaningful join name, either when creating, or when editing the join.
-
Under Table 1, choose the table you want to create a join from (origin table).
-
Under Table 2, choose the destination table or View for the other end of the join.
-
Choose the matching columns under each table. These columns must use the same data type. [Optional] You can select multiple columns for the same join. To add another pair of matching columns to the join definition, select +Add columns.
-
Specify the join type; see Join types.
-
Specify the join cardinality; see Join cardinality.
-
Select Create join.
New table join interface
You can try a new way of creating table joins which will become the default in a future release.
To create a join using the new join interface, do the following:
-
Select Data in the top menu and choose Tables.
-
Find your table through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
To select the table for adding joins, click its name in the list. You will see the Columns view of the table.
Generally, creating a many-to-one join from a fact table to a dimension table simplifies your search. -
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins (if any) from the table appears.
-
Select + Add join.
The Create Join page appears.
You cannot create range joins in the UI. You must use TML. -
In the Join name field, enter a name for your join.
-
Under Table 1, choose the table you want to create a join from (origin table).
-
Under Table 2, choose the destination table or View for the other end of the join. This is usually a dimension table.
-
Choose the matching columns under each table. These columns must use the same data type.
-
[Optional] You can select multiple columns for the same join. To add another pair of matching columns to the join definition, select +Add column.
-
Specify the join type; see Join types.
-
Specify the join cardinality; see Cardinality.
-
Select Save.
You can now see the updated view of the schema. You can also see the detailed information about all Joins. Note that after creating the join, you may change its name, type, or cardinality by selecting the edit icon. You can also change the location and size of tables and joins in the model. You can move or resize tables and joins to display the best visual representation of the model. If you want to change the data source or column being joined, you must delete the join and create a new one.
Proceed to create all necessary table joins, to support your data requirements.
Creating a join from a worksheet or view
To create a join from a worksheet:
-
To find your worksheet, select Data on the top menu, and choose Worksheets.
-
Find your worksheet through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
To select the worksheet for adding joins, click its name in the list.
-
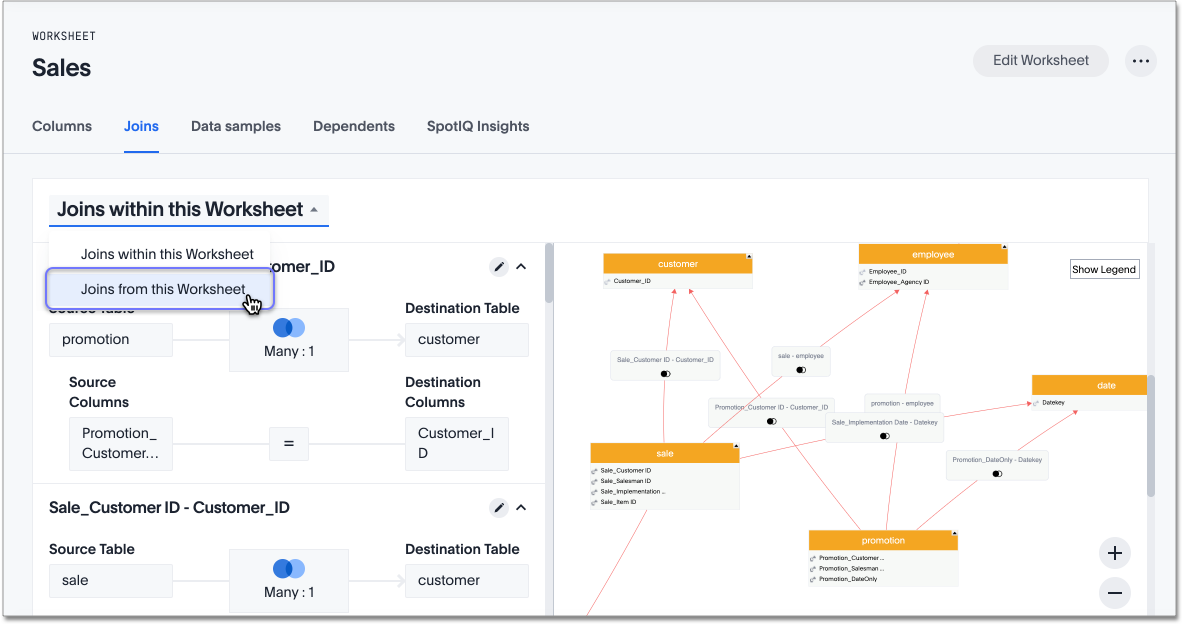
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins within the worksheet appears.
-
To view the joins between this worksheet and other data sources, select Joins within this worksheet, and choose Joins from this worksheet.
-
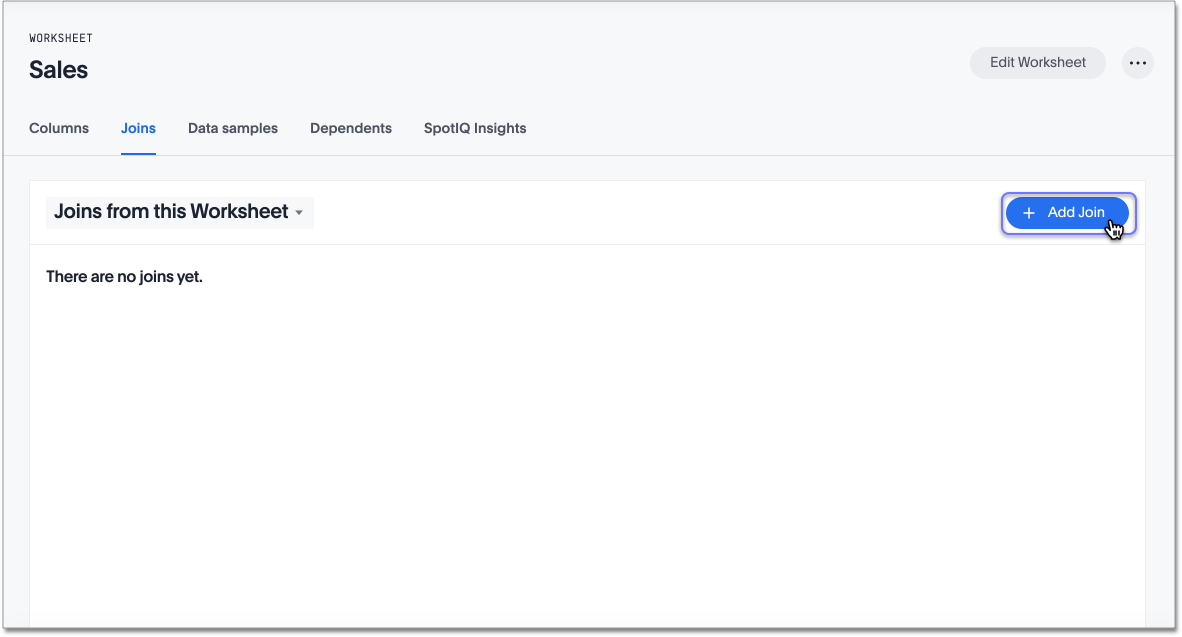
To start creating a join, select + Add Join on the upper-right side of the screen.
-
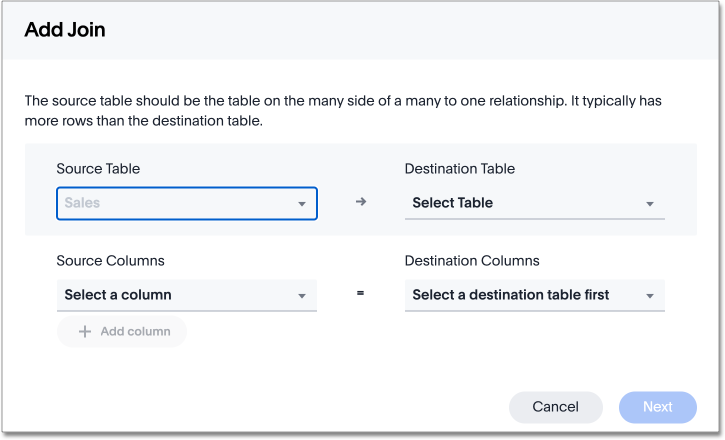
In the Add Join dialog, choose the destination table or View for the other end of the join.
-
Choose the matching columns under each table. These columns must use the same data type. [Optional] You can select multiple columns for the same join. To add another pair of matching columns to the join definition, select + Add columns.
-
Specify the join type; see Join types.
-
Specify the join cardinality; see Join cardinality.
-
Select Create join.
Modifying joins
ThoughtSpot allows you to edit the name, join type, and cardinality through the web interface. This allows you to change a many-to-one join to one-to-one. To reverse the join cardinality, you must delete the join and create it again with the opposite cardinality. Deleting the join doesn’t delete the dependent objects, but it does make them unusable until you create another join. To change the columns that define a join, you must delete the join and create a new one.
Editing a join from a table
To edit a join between tables:
-
Select Data in the top menu, and choose Tables.
-
Find your table through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
To select the table for adding joins, click its name in the list. You will see the Columns view of the table.
-
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins from the table appears.
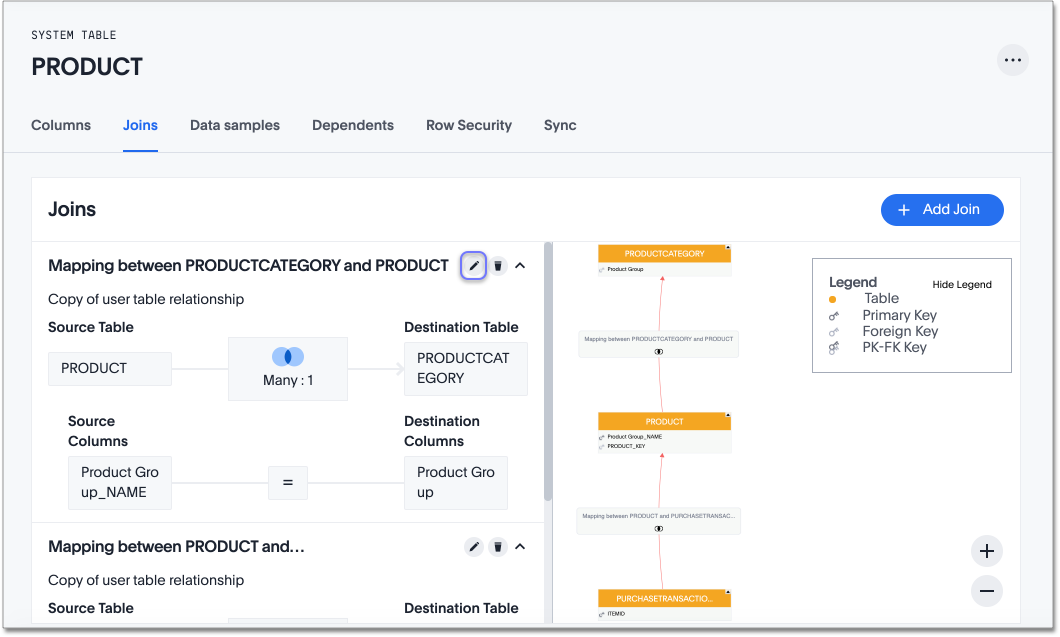
-
Select the edit icon to the right of the name of the join you want to modify. The Edit join page appears.
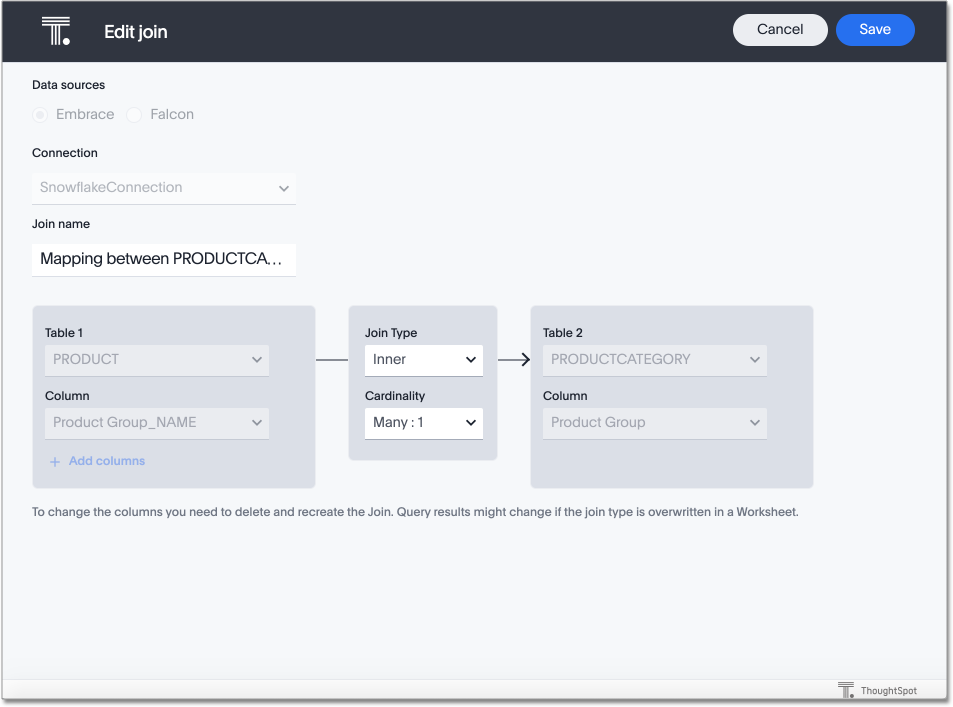
-
Make the desired changes to the name, type, or cardinality of the join. This allows you to change a many-to-one join to one-to-one. To reverse the join cardinality, you must delete the join and create it again with the opposite cardinality. Deleting the join doesn’t delete the dependent objects, but it does make them unusable until you create another join.
-
Select Save.
Editing a join from a worksheet or view
To edit a join from a worksheet or view:
-
Select Data in the top menu, and choose Worksheets.
-
Find your worksheet through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
To select the worksheet, select its name in the list.
-
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins within the worksheet appears.
-
To view the joins between the worksheet and other data sources, select Joins within this worksheet, and choose Joins from this worksheet.
-
Select the edit icon to the right of the name of the join you want to modify. The Edit join window appears.
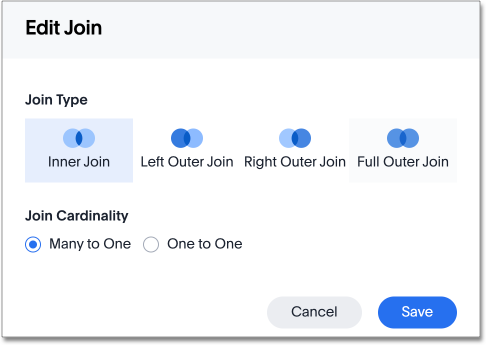
-
Make the desired changes to the join type or cardinality. This allows you to change a many-to-one join to one-to-one. To reverse the join cardinality, you must delete the join and create it again with the opposite cardinality. Deleting the join doesn’t delete the dependent objects, but it does make them unusable until you create another join.
-
Select Save.
Deleting a join
To delete a join:
-
Select Data in the top menu.
-
Find the origin table, worksheet, or view of the join you want to delete through browsing, Search, or selecting the appropriate Tag(s).
-
Select the name of your origin table, worksheet or view in the list.
-
Select the Joins tab. The list of existing joins from the table, worksheet, or view appears.
If you want to delete an external join from a worksheet, you must click Joins within this worksheet under the Joins tab and select Joins from this worksheet. 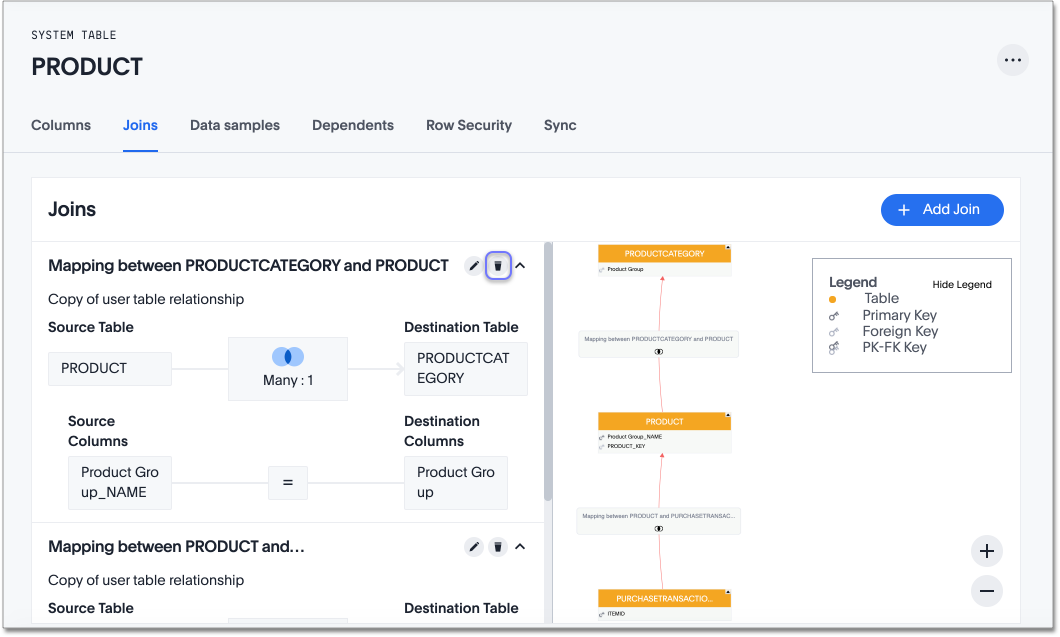
-
Select the delete icon to the right of the join name. The Confirm delete window appears.
If the join has dependents, a different window appears, warning you that deleting this join makes the dependent objects stop working until you recreate the join later. However, ThoughtSpot doesn’t delete the dependent objects. You can use this functionality to reverse the join cardinality or otherwise edit a join without deleting its dependents.
-
Select Delete.
Delete or edit a relationship that has dependents
If a relationship has dependents, and you need to delete the relationship, edit or reverse the join cardinality, or edit the join keys or condition, the process is slightly different. After you delete a relationship with dependents, the dependents still exist, but stop working until you create the relationship again and fix the first-level dependents, either by selecting Edit worksheet > Fix worksheet for worksheets, or selecting Save for answers or Liveboards.
Only delete a relationship with dependents if you plan to edit the relationship and add it in again, or if you can also delete the dependents.
For example, you can use this functionality to reverse the join cardinality.
Reverse join cardinality
You can use the delete functionality to reverse or change the join cardinality for a join that has dependents. To reverse the join cardinality, follow these steps:
-
Select the Delete icon to the right of the join name.
-
A warning appears, telling you that deleting the join will make dependent objects stop working. Make a note of these objects.
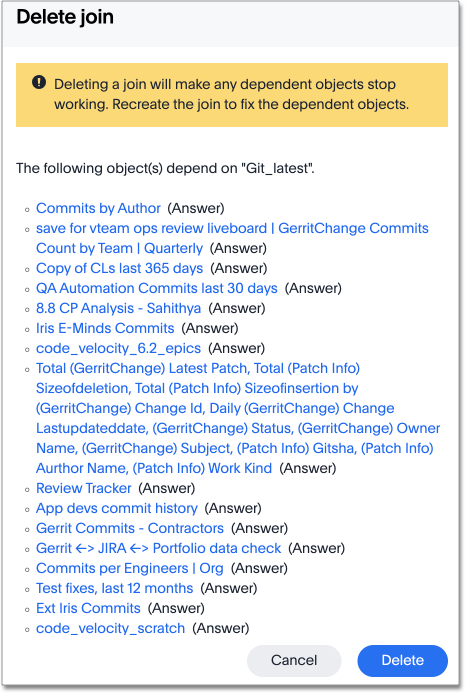
-
-
Select Delete.
-
At this point, the dependents still exist, but are unusable.
-
Create the join again, with the opposite cardinality, and any other changes you must make.
-
Navigate to any first-level dependents for the join. For example, you may have a join between two tables. You created a worksheet based on these two tables and the join. You created several answers based on the worksheet. Only the worksheet is a first-level dependent. The answers are not first-level dependents.
-
If the first-level dependents are worksheets, select Edit worksheet for each worksheet, select Fix worksheet in the upper-right corner, and then Save the worksheets. If the first-level dependents are answers or Liveboards, select Save for each object. Now all dependents are usable.
If a join doesn’t have dependents, you can change the join cardinality by editing the join. This allows you to change a many-to-one join to one-to-one. To reverse the join cardinality, you must delete the join and create it again with the opposite cardinality.
Related information



